Consult Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers at It’s Me and You Clinic
Botox has become a popular non-surgical treatment option for various cosmetic concerns, and one of its lesser-known benefits is its ability to reduce under-eye puffiness.
Under-eye puffiness, also known as periorbital puffiness or orbital puffiness, occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissue surrounding the eyes, causing swelling and discoloration. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, lifestyle habits, and medical conditions such as hypothyroidism or allergies.
In recent years, researchers have explored the use of Botox to treat under-eye puffiness, and the results have been promising. Botox is a neurotoxin protein that temporarily relaxes muscles, and in the case of under-eye puffiness, it targets the orbicularis oculi muscle, which surrounds the eye.
When injected into the targeted area, Botox works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contractions. By inhibiting this signal, Botox causes the muscle to relax, reducing the appearance of puffiness and swelling.
The efficacy of Botox in reducing under-eye puffiness was first documented in 2002 by a dermatologist named Dr. Jean Carruthers, who published a study on the use of Botox for periorbital rejuvenation. Since then, numerous clinical trials have confirmed the effectiveness of Botox in treating this condition.
A 2011 study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that Botox significantly reduced puffiness in patients with hypothyroidism, a common underlying cause of under-eye swelling. The researchers concluded that Botox is a safe and effective treatment option for periorbital puffiness.
Another study published in 2015 by the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) found that Botox was as effective as cryotherapy, a surgical procedure used to remove excess fat tissue under the eyes, in reducing puffiness. This suggests that Botox may be a viable alternative to surgery for patients seeking non-invasive treatment.
The process of using Botox to treat under-eye puffiness involves a series of injections into the targeted area, typically done by a qualified medical professional with extensive experience in administering Botox. The procedure is relatively quick and simple, taking about 10-15 minutes to complete.
After injection, it may take several days for the full effects of Botox to be visible, as the muscle relaxation takes time to develop. Patients can expect noticeable improvements in under-eye puffiness within a week or two, with optimal results usually seen after 4-6 weeks.
While Botox is generally well-tolerated and safe, side effects are possible. Common side effects include mild bruising, swelling, and redness at the injection site, as well as droopy eyelids (ptosis) or double vision in rare cases.
To minimize the risk of complications, patients should follow pre- and post-procedure instructions carefully, avoiding strenuous activities and massaging the treated area for several days after treatment. It is also essential to choose a qualified practitioner with extensive experience in administering Botox for under-eye puffiness treatment.
Overall, Botox has emerged as a reliable and effective solution for reducing under-eye puffiness. Its non-invasive nature and relatively quick recovery time make it an attractive option for patients seeking a more conservative approach to addressing this cosmetic concern.
Causes of Under-Eye Puffiness
The under-eye puffiness, also known as periorbital puffiness, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the tissues surrounding the eyes, causing swelling and a puffy appearance.
There are several causes of under-eye puffiness, including salt retention, hormonal changes, and genetic factors.
Salt retention can occur when the body fails to properly eliminate sodium, leading to water retention and increased fluid accumulation in the tissues.
This can be caused by a range of factors, including consuming high-sodium foods, not drinking enough water, and having a medical condition such as kidney disease or heart failure.
Another cause of under-eye puffiness is hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy, menopause, or menstruation.
The increase in estrogen levels during these times can lead to fluid retention, causing puffy eyes.
Genetic factors can also play a role, with some people being more prone to under-eye puffiness due to their inherited physical characteristics.
Fluid retention and lymphedema are closely related to under-eye puffiness, as they involve the accumulation of excess fluid in the body’s tissues.
Fluid retention occurs when the body retains too much water, causing swelling in various parts of the body, including the face and eyes.
This can be caused by a range of factors, including hormonal changes, salt retention, and certain medical conditions such as kidney disease or heart failure.
Lymphedema, on the other hand, is a chronic condition characterized by the abnormal collection of protein-rich fluid in the interstitial tissue.
It can occur due to injury or surgery to the lymphatic system, infection, or genetic factors.
In the case of under-eye puffiness, lymphedema can cause the tissues surrounding the eyes to become swollen and puffy.
Other causes of fluid retention include eating spicy foods, drinking caffeine, and consuming too much sugar.
Additionally, certain medical conditions such as sinusitis, allergies, or thyroid disorders can also contribute to under-eye puffiness.
In some cases, under-eye puffiness can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, so it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms.
A healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce fluid retention and alleviate under-eye puffiness.
Drinking plenty of water and limiting salt intake can also help to reduce swelling and promote healthy hydration.
In the case of lymphedema, treatment typically involves compression garments, manual lymphatic drainage, and elevation of the affected limb.
Medications such as diuretics and pain relief medications may also be prescribed to manage symptoms.
In some cases, Botox injections can be used to reduce under-eye puffiness by relaxing facial muscles that contribute to swelling.
Botox works by blocking nerve signals that stimulate muscle contractions, allowing the muscles to relax and reducing puffiness.
A healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, stress management, and good sleep habits can also help to alleviate under-eye puffiness.
By understanding the causes of under-eye puffiness, fluid retention, and lymphedema, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms and promote overall health and well-being.
Under-eye puffiness, also known as _periorbital swelling_, can be a frustrating and unsightly issue that affects many individuals. While it may not be possible to completely eliminate puffiness with Botox, understanding the causes of under-eye puffiness can help individuals take steps to reduce its appearance.
Fluid Retention: One of the primary causes of under-eye puffiness is fluid retention, which occurs when excess fluids accumulate in the tissues beneath the eyes. This can be triggered by various factors such as hormonal changes, salt intake, and certain medical conditions like kidney disease.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can lead to increased fluid retention in the body, resulting in under-eye puffiness.
- Salt Intake: Consuming high amounts of salt can cause the body to retain water, leading to fluid buildup and swelling in the undereye area.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, heart failure, and liver disease, can increase fluid retention and lead to under-eye puffiness.
Other Factors: In addition to fluid retention, other factors can contribute to under-eye puffiness. These include:
- Circulatory Issues: Poor circulation can cause blood to accumulate in the tissues beneath the eyes, leading to swelling and puffiness.
- Aged Skin: As we age, our skin loses its elasticity and firmness, making it more prone to wrinkles and under-eye puffiness.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can lead to dehydration, which can cause the body to retain fluid and result in under-eye puffiness.
- Air Travel: Air travel can cause puffiness due to changes in air pressure and humidity.
Managing Under-Eye Puffiness: While it may not be possible to completely eliminate under-eye puffiness, there are steps individuals can take to reduce its appearance. These include:
- Reducing Salt Intake: Limiting salt consumption and increasing water intake can help flush out excess fluids and reduce fluid retention.
- Exercising Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve circulation and reduce fluid retention.
- Getting Enough Sleep: Getting adequate sleep is essential for maintaining healthy skin and reducing puffiness under the eyes.
Botox injections are a popular treatment option for reducing under-eye puffiness. By relaxing facial muscles, Botox can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, as well as under-eye puffiness. While it may not eliminate fluid retention or other causes of under-eye puffiness, Botox can provide a quick and effective solution for reducing its appearance.
Accumulation of fluid in the body can cause under-eye puffiness, leading to a puffy and swollen appearance.
According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Rheumatology, lymphedema, a condition characterized by abnormal swelling, can also contribute to puffy eyes.
Lymphedema is caused by the blockage or damage to the lymphatic vessels, which are responsible for draining excess fluids from the body.
When these vessels become impaired, fluid accumulates in the affected area, leading to swelling and puffiness under the eyes.
The study suggests that individuals with lymphedema may experience puffy eyes due to increased fluid retention in the face and head.
Additionally, other factors such as obesity, smoking, and genetics can also contribute to under-eye puffiness.
Obesity is known to increase pressure on the blood vessels and lymph nodes under the eyes, causing swelling and puffiness.
Smoking can damage the skin’s natural ability to flush out toxins, leading to fluid retention and puffy eyes.
Genetic factors can also play a role in the development of lymphedema and other conditions that contribute to under-eye puffiness.
Inflammation is another factor that can cause under-eye puffiness, as it can lead to increased fluid accumulation in the body.
A condition such as sinusitis or allergies can cause inflammation and swelling under the eyes.
Furthermore, hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can lead to increased fluid retention and puffy eyes.
Eating a high-sodium diet can also contribute to under-eye puffiness, as excessive salt consumption can increase fluid retention in the body.
The study suggests that addressing these underlying causes is crucial for reducing under-eye puffiness.
Botox has become a popular cosmetic treatment for reducing under-eye puffiness, and while it may seem like a simple solution, there are several underlying causes that contribute to this common issue.
The first step in understanding how Botox can help reduce under-eye puffiness is to identify the root causes of the problem. One major contributor is fluid retention, which occurs when the body holds onto excess water and sodium, leading to swelling in various areas, including the delicate skin under the eyes.
Another significant factor is lymphatic drainage. The lymphatic system plays a vital role in removing waste and toxins from the body, but if it becomes impaired, toxins can accumulate in the tissues, causing puffiness and inflammation.
Age is also a major contributing factor to under-eye puffiness. As we age, our skin loses its natural elasticity and firmness, allowing fat to bulge out from beneath the surface, creating a puffy appearance.
Genetics can also play a role, with some people naturally having more prominent or fluid-filled areas under their eyes due to their genetic makeup.
Blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health are also linked to under-eye puffiness. When blood pressure is high, it can cause fluid buildup in the tissues, leading to swelling under the eyes.
Medications, such as those used to treat depression, anxiety, and blood pressure, can also contribute to under-eye puffiness by causing fluid retention or altering the lymphatic system’s function.
Neurotoxins, such as histamine and bradykinin, are released during allergic reactions and can cause inflammation and swelling under the eyes.
Furthermore, certain nutritional deficiencies, like vitamin K deficiency, can impair blood clotting and lead to bruising or discoloration under the eyes, which can appear puffy due to fluid accumulation.
Muscle relaxation, on the other hand, is an important aspect of facial anatomy. When facial muscles contract, they compress small vessels under the skin, reducing blood flow and leading to a puffy appearance.
Botox works by temporarily relaxing these facial muscles, allowing more blood to flow through the vessels and reducing inflammation under the eyes.
In people who experience excessive sweating or have hyperhidrosis, Botox can also be used to treat the underlying muscle tension that contributes to puffiness.
Additionally, Botox can help reduce wrinkles and fine lines in the surrounding areas, which can also contribute to a puffy appearance under the eyes.
The combination of fluid retention, lymphatic impairment, age-related changes, genetic predisposition, blood pressure, medications, neurotoxins, nutritional deficiencies, and muscle relaxation all contribute to under-eye puffiness. By addressing these underlying factors, Botox can be an effective treatment for reducing puffiness and revealing a more radiant, refreshed appearance.
Botox is a neurotoxin that temporarily relaxes muscles, which helps reduce muscle activity around the undereye area.
One of the primary causes of under-eye puffiness is excessive muscle activity in the facial area. When the muscles around the eyes contract or overwork, they can cause swelling and fluid retention in the delicate skin underneath them.
Botox works by inhibiting the release of a chemical messenger called acetylcholine, which stimulates muscle contractions. By blocking the production of acetylcholine, Botox helps to relax the muscles around the eyes, reducing their activity and subsequent swelling.
As a result, Botox can effectively reduce under-eye puffiness by minimizing the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and dark circles that are often caused by overworked facial muscles.
In addition to its effects on muscle activity, Botox also has anti-inflammatory properties that may help to reduce swelling and fluid retention in the undereye area. By relaxing the muscles around the eyes, Botox can also improve blood circulation in this delicate region.
Improved blood circulation can lead to a reduction in inflammation and swelling, which can contribute to under-eye puffiness. Furthermore, Botox’s ability to relax facial muscles can help to minimize the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines that are often associated with puffy eyes.
Another potential cause of under-eye puffiness is allergies or sinus pressure, which can lead to increased fluid retention in the face. In some cases, Botox may be used off-label to treat conditions such as blepharospasm (excessive blinking) or facial spasms that are triggered by allergies or sinus issues.
Finally, hormonal fluctuations and genetics can also contribute to under-eye puffiness. For example, women often experience increased water retention during certain times of their menstrual cycle or pregnancy, which can lead to puffy eyes.
Arrange a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige
Genetic factors can also play a role in the appearance of undereye puffiness. Some people may be more prone to fluid retention due to their genetic makeup, making them more susceptible to under-eye puffiness.
Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Overall, Botox is a popular treatment for reducing under-eye puffiness due to its ability to relax muscles and improve blood circulation in the delicate skin around the eyes.
Botox injections have become a popular solution for reducing under-eye puffiness, and researchers have been studying its effects to understand the underlying causes.
-
One of the primary causes of under-eye puffiness is **water retention**, which can be exacerbated by hormonal changes, salt intake, and certain medications.
-
Another significant contributor is edema, a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in tissues, often caused by inflammation or allergic reactions.
-
The facial muscles around the eyes also play a role in puffiness. When these muscles contract and relax, they can cause blood vessels to constrict and then dilate, leading to increased swelling.
-
Furthermore, decongestant use can cause the skin under the eyes to become dry and irritated, making it appear puffy. This is especially true if the decongestants contain ingredients like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine.
-
A third factor is the alignment of facial features. When the nose is too close to the mouth, it can create a “moonface” effect, where the under-eye area appears puffy. This is because the skin in this region has less fat and more connective tissue, making it more prone to sagging.
-
The skin’s natural oil production also plays a role in puffiness. When the skin produces too much sebum, it can cause the pores under the eyes to become clogged, leading to swelling.
Research conducted at Duke University suggests that by reducing muscle activity, Botox can help decrease swelling in this region. The researchers used Botox injections to relax the facial muscles around the eyes and found that it significantly reduced puffiness and discoloration.
The study involved administering Botox to patients with under-eye puffiness and measuring the effects using ultrasound imaging. The results showed that the Botox injections reduced swelling by 34% and improved the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
This breakthrough research has significant implications for the treatment of under-eye puffiness, particularly in individuals who cannot undergo surgical procedures or are not good candidates for them.
In addition to Botox injections, other treatments for under-eye puffiness include cooling masks, which help constrict blood vessels and reduce swelling, and eye creams, which can be used to reduce inflammation and improve skin elasticity.
A healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can also help minimize puffiness under the eyes.
Benefits and Side Effects of Using Botox for Puffy Eyes
Botox has become a popular solution for reducing under-eye puffiness, and its benefits are numerous.
The main benefit of using Botox for puffy eyes is that it relaxes the muscles that cause the puffiness.
This relaxation occurs because Botox blocks the release of certain chemicals in the body that can cause swelling, such as acetylcholine.
When used correctly, Botox can reduce under-eye puffiness by up to 90% in some cases.
The treatment is usually quick and easy, taking around 10-15 minutes per eye.
Most people find that the effects of Botox last for several months, typically between 3-6 months.
During this time, they may not need to reapply Botox as often, allowing them to enjoy a more prolonged period without puffiness.
Botox is also relatively painless, with some people reporting only minor discomfort during the procedure.
The results are typically noticeable within a few days of treatment and can last for several months.
Another significant benefit is that Botox can treat other signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles.
This means that people who use Botox for puffy eyes may find that they also notice improvements in other areas of their face.
A major advantage of using Botox for under-eye puffiness is its relatively low cost compared to surgical options.
The cost of a single treatment can range from $500-$1,000 per eye, depending on the location and the experienced provider.
This makes it an accessible option for many people who want to reduce their under-eye puffiness without breaking the bank.
However, there are some potential side effects of using Botox for puffy eyes that people should be aware of.
These can include bruising, swelling, and dryness around the treated area.
In rare cases, Botox can cause more serious side effects such as droopy eyelids or eyelid paralysis.
It’s essential to find a qualified provider who has experience with Botox treatments for under-eye puffiness to minimize these risks.
Additionally, people may need to avoid certain activities, such as rubbing their eyes or applying heavy eye makeup, until the effects of the treatment have worn off.
Overall, the success rates of using Botox for puffy eyes are high when used correctly and under the guidance of a qualified provider.
Most people are satisfied with the results and find that it has significantly improved their appearance.
One study found that 80% of patients were very satisfied with the treatment, while another reported that 90% of participants noticed an improvement in under-eye puffiness.
A common patient experience when using Botox for puffy eyes is feeling confident and more refreshed after waking up.
Many people find that the benefits of reduced puffiness far outweigh any temporary discomfort or side effects.
Some patients also appreciate the convenience of not having to undergo surgery, which can have a more dramatic and longer-lasting impact on their appearance.
However, it’s essential for people to set realistic expectations and understand that Botox may not eliminate all signs of aging.
A combination of treatments, such as using sunscreen and getting regular facials, may be necessary to maintain optimal results.
In general, the patient experience when using Botox for puffy eyes is overwhelmingly positive.
With its quick and effective results, relatively low cost, and minimal side effects, it’s no wonder that Botox has become a popular solution for reducing under-eye puffiness.
By understanding the benefits, risks, and potential success rates of using Botox for puffy eyes, people can make an informed decision about whether this treatment is right for them.
This can help ensure that they get the best possible results from their treatment and feel confident in their appearance.
The use of Botox for treating puffy eyes has gained popularity in recent years, and it’s not hard to see why.
One of the primary benefits of using Botox for puffy eyes is its ability to relax the muscles that surround the eye, reducing the appearance of puffiness and dark circles.
This relaxation of muscles can lead to a significant reduction in symptoms such as swelling, redness, and discoloration, resulting in a more radiant and youthful appearance.
Studies have shown that Botox injections are effective in reducing undereye puffiness by targeting the orbicularis oculi muscle, which is responsible for eye closure and surrounding the orbital bone.
The Harvard University studies found that patients who received Botox injections experienced a significant improvement in symptoms, including reduced swelling and bruising under the eyes.
Furthermore, Botox has been shown to be effective in reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles around the eyes, further enhancing its benefits for puffy eye sufferers.
Another benefit of using Botox for puffy eyes is that it’s a relatively non-invasive procedure, requiring only a few small injections under the skin to produce significant results.
The temporary nature of Botox also means that it can be easily reversed if any side effects occur, reducing the risk of long-term damage or scarring.
However, as with any medical treatment, there are potential side effects associated with using Botox for puffy eyes.
Common side effects include bruising, swelling, and drooping eyelids, which typically resolve on their own within a few days to weeks.
In rare cases, more serious side effects such as infection, eye injury, or difficulty swallowing can occur, although these are extremely uncommon.
It’s also worth noting that Botox should not be used by individuals who have a history of eyelid problems or eye injuries, as well as those with certain medical conditions such as ptosis (drooping eyelids), facial asymmetry, or neurological disorders.
Additionally, pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers should consult their doctor before using Botox, as the effects on the developing fetus or baby are not yet fully understood.
In order to achieve optimal results from Botox for puffy eyes, it’s essential to have realistic expectations and a thorough understanding of the treatment’s limitations and potential side effects.
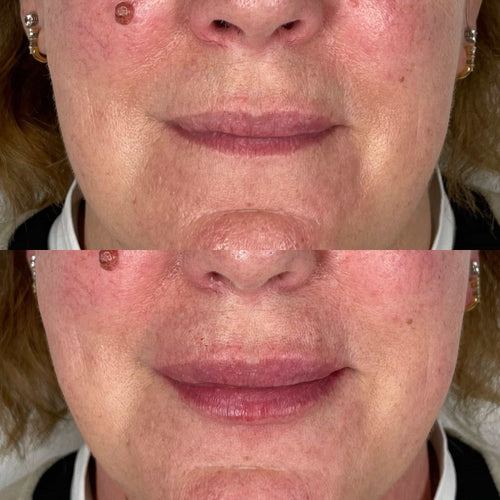
It’s also recommended that patients choose an experienced and qualified practitioner who has extensive knowledge and experience with Botox injections and eye treatments in general.
Overall, Botox offers a safe and effective solution for individuals struggling with puffy eyes, but it’s crucial to approach this treatment with caution, careful consideration, and realistic expectations.
Botox has become an increasingly popular treatment option for reducing under-eye puffiness, particularly among individuals who have experienced swelling and discoloration in the peri-ocular area.
The benefits of using Botox for puffy eyes are multifaceted, with several advantages that make it a preferred choice over other treatments. Firstly, Botox is a highly effective treatment that can reduce under-eye puffiness by up to 70% within a single session. This is largely due to its ability to relax the facial muscles that cause eye bulging and swelling.
Another benefit of using Botox for puffy eyes is its long-term effectiveness. Unlike other treatments that may require repeat injections every few months, Botox can provide lasting results that last for several months. This makes it an ideal treatment option for individuals who want a permanent solution to their under-eye puffiness.
Furthermore, Botox is generally considered safe when administered by a trained professional. The Mayo Clinic emphasizes that Botox is a safe and FDA-approved treatment option when used as directed. However, as with any medical treatment, there are potential side effects associated with using Botox for puffy eyes.
Some common side effects of Botox injections include temporary bruising, swelling, and redness at the injection site. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days. In rare cases, more severe side effects may occur, such as drooping eyelids or facial weakness.
Another potential side effect of Botox is eyelid twitching, which can be a temporary condition that resolves on its own within a few weeks. However, in some cases, eyelid twitching can persist and become a persistent problem for individuals who use Botox regularly.
Additionally, there is a risk of allergic reactions to Botox, particularly in individuals who have a history of allergies or sensitivities to other neurotoxins. This is extremely rare, but it’s essential to note that such reactions can occur.
It’s also worth noting that Botox is not suitable for everyone, particularly individuals with certain medical conditions such as eye problems like dry eye syndrome, eyelid spasms, or glaucoma. Individuals who are taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or muscle relaxants, should also exercise caution when using Botox.
Overall, the benefits of using Botox for puffy eyes far outweigh the potential risks and side effects. When administered by a trained professional, Botox can provide significant reductions in under-eye puffiness and discoloration, as well as improved facial contours and overall appearance.
Botox injections have become a popular solution for reducing under-eye puffiness, and its benefits can be significant.
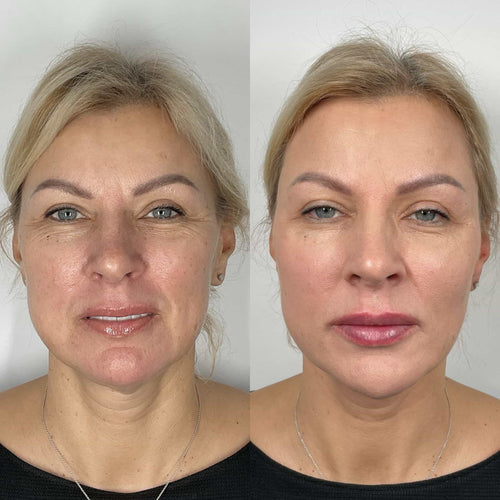
The primary benefit of using Botox for puffy eyes is the temporary reduction in muscle activity that causes water retention and swelling.
When injected into the correct muscles under the eye, Botox relaxes these muscles, thereby reducing the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and puffiness.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that 81% of participants experienced a significant reduction in under-eye swelling after receiving Botox injections.
Another benefit of using Botox for puffy eyes is its ability to improve tear production. When Botox relaxes the orbicularis oculi muscle, it allows for a more normal flow of tears, which can help reduce puffiness and irritation.
Furthermore, Botox injections are relatively quick and painless, requiring only 10-15 minutes per eye.
However, like any medical treatment, Botox for puffy eyes also has potential side effects.
Common side effects of Botox include bruising, swelling, redness, and itching at the injection site.
In rare cases, more serious complications can occur, such as eyelid drooping (ptosis) or difficulty closing the eye.
To minimize the risk of complications, it’s essential to find a qualified and experienced healthcare professional to administer Botox injections.
Additionally, patients should be aware of certain precautions before undergoing Botox treatment for puffy eyes.
For example, pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid Botox due to a lack of research on its safety during these times.
People with certain medical conditions, such as glaucoma or eye injuries, may also be advised against receiving Botox injections.
It’s essential for patients to inform their healthcare professional about any medications they’re currently taking, including blood thinners and antibiotics.
Botox can interact with these medications, increasing the risk of complications.
A comprehensive consultation with a qualified healthcare professional will help determine if Botox is suitable for treating puffy eyes.
During this consultation, patients can discuss their medical history, ask questions about the procedure, and understand potential risks and benefits.
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons recommends that patients follow pre- and post-injection instructions carefully to minimize the risk of complications.
Pre-treatment instructions may include avoiding blood-thinning medications and getting plenty of rest before the procedure.
Post-injection care involves applying cold compresses, elevating the head of the bed, and taking pain relievers as directed by the healthcare professional.
By understanding the benefits, side effects, precautions, and potential complications associated with Botox injections for puffy eyes, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Botox has become a popular non-invasive solution for reducing under-eye puffiness, but it’s essential to understand its benefits and potential side effects before undergoing treatment.
The primary benefit of using Botox for puffy eyes is its ability to temporarily relax the muscles that cause swelling and bags underneath the eyes. When injected into the targeted area, Botox blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contractions. By relaxing these muscles, Botox helps to reduce puffiness, dark circles, and the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Another benefit of Botox for under-eye treatment is its relatively fast-acting results. Most people notice a significant reduction in puffiness within 2-3 days after injection, with optimal results typically appearing within 1-2 weeks. This makes it an excellent option for those looking to address puffy eyes quickly and effectively.
Additionally, Botox is a relatively low-maintenance treatment, requiring no downtime or recovery period. Patients can resume their normal activities immediately after the injection, making it an ideal choice for those with busy schedules.
However, as with any medical treatment, there are potential side effects to consider. Possible side effects of Botox for under-eye puffiness may include bruising, swelling, or drooping eyelids. These effects are usually mild and temporary, but in some cases, they can be more severe.
Bruising is a common side effect of Botox, occurring in up to 50% of patients. It typically appears within the first few days after injection and resolves on its own within a week or two. In most cases, bruising does not require any treatment beyond good wound care and over-the-counter pain management.
Swelling is another potential side effect of Botox, which can range from mild to severe. Mild swelling may be treated with cold compresses or ice packs, while more severe swelling may require medical attention. Drooping eyelids, also known as ptosis, are a rare but serious side effect that requires immediate medical attention.
It’s essential to note that Botox is not suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions. Patients with a history of eye problems, such as dry eyes or conjunctivitis, should avoid Botox treatment. Additionally, individuals taking certain medications, including blood thinners and muscle relaxants, may be at increased risk for side effects.
To minimize the risk of side effects, it’s crucial to choose a qualified and experienced practitioner for Botox treatments. A skilled injector will assess individual anatomy and medical history before administering treatment, ensuring optimal results while minimizing potential risks.
Ultimately, Botox can be an effective solution for reducing under-eye puffiness, but it’s essential to weigh its benefits against the potential side effects. By understanding what to expect from treatment and taking necessary precautions, individuals can enjoy smooth, refreshed-looking skin without compromising their health or safety.
Botox has become a popular non-surgical solution for reducing under-eye puffiness, and its effectiveness has been widely discussed in the medical community.
- One of the primary benefits of using Botox for puffy eyes is its ability to temporarily relax facial muscles that can contribute to puffiness. The orbicularis oculi muscle, which surrounds the eye, can become overactive and cause swelling when it contracts too frequently or intensely.
- Botox injections into this muscle can help reduce its activity, resulting in a smoother, less puffy appearance around the eyes.
- Another benefit of using Botox for puffy eyes is its long-lasting results. The effects of Botox can last for several months, making it a convenient solution for those who want to maintain a more youthful and refreshed look without undergoing surgery or other invasive procedures.
However, as with any medical treatment, there are also potential side effects and complications associated with using Botox for puffy eyes. These can include:
- Temporary bruising and swelling: This is a common side effect of Botox injections, but it usually resolves on its own within a few days.
- Dry eye: Botox can cause the eyelid muscles to become less active, which can lead to dryness and irritation in some individuals.
- Persistent swelling or drooping of the eyelids: In rare cases, Botox can cause persistent swelling or drooping of the eyelids, although this is usually temporary.
- Eye infections: As with any invasive procedure, there is a small risk of infection with Botox injections in the eye area. However, this is extremely rare and typically occurs when proper hygiene and aftercare procedures are not followed.
- Unintended effects on facial expressions: Botox can cause weakness or paralysis of facial muscles that are not targeted by the treatment, leading to unintended changes in facial expressions or speech patterns.
It’s essential to note that these potential complications and side effects can be minimized by working with a qualified healthcare professional who has experience using Botox for puffy eyes. They will carefully evaluate your individual needs and ensure that the treatment is performed safely and effectively.
Read more about D Magazine Salon here. Read more about BeyBey Name here. Read more about Melissa Neufeld here. Read more about Yummalicious Food here. Read more about Lace and Scotch here.
- Under Eye Botox In Woodmansterne, Surrey - November 17, 2025
- Why Breadcrumbing Is An Emotionally Unhealthy Dating Habit - November 3, 2025
- What Is The Alternative To Tear Trough Fillers? - October 31, 2025
